If the clarinet had a secret doorway into smoky flamenco nights and ancient church chants, it would be the E Phrygian scale. On Bb clarinet, this scale feels like a whisper from another century: exotic, a little haunted, and endlessly expressive.
Receive a free PDF of the chart with clarinet fingering diagrams for every note!
The E Phrygian scale on Bb clarinet is a seven note minor-mode scale built on E that uses a flattened second degree. It sounds dark and Spanish, and it helps clarinetists shape expressive solos, haunting melodies, and dramatic film-style phrases with confidence and control.
The sound and story of the E Phrygian scale
The E Phrygian scale lives in that beautiful space between mystery and fire. It shares its notes with C major, but because E is the center of gravity, everything tilts toward tension. The flattened second (F natural over E) gives it that unmistakable, almost vocal cry you hear in Spanish guitar, oud melodies, and old church modes.
On Bb clarinet, that low written F natural leaning into E feels like bending a ray of light. It has the depth of Brahms, the edge of Astor Piazzolla, and the smoky warmth of a Benny Goodman ballad. You do not just play E Phrygian. You confess something with it.
The E Phrygian scale has the same notes as C major, but with E as tonic and F as a flattened second. That single semitone at the start creates the unmistakable Spanish color clarinetists love.
From monasteries to flamenco clubs: a short journey
The Phrygian mode goes back to medieval plainchant and Renaissance counterpoint, long before the Boehm-system Bb clarinet was even a sketch on a workbench. Church singers and organists used this mode to suggest holy awe, fear, and humility. E Phrygian, in particular, sat beautifully on early instruments like the recorder and shawm.
By the baroque era, clarinet ancestors like the chalumeau were gaining ground. Players close to the traditions that inspired Anton Stadler and Heinrich Baermann would have known Phrygian-flavored lines from motets, cantatas, and early orchestral pieces by composers like Vivaldi and Corelli. While these composers did not label phrases “E Phrygian” the way we do today, they constantly leaned on that brooding half step in their melodic writing.
As the clarinet entered classical and romantic orchestras, composers such as Mozart, Weber, and later Brahms wrote in keys where the Phrygian color appears as a borrowed mode. Inside the Mozart Clarinet Concerto, K. 622, listen to the slow movement and imagine rephrasing some passages with an E Phrygian thought in mind: the clarinet line suddenly sounds more ancient and more vocal.
Famous clarinet voices who loved this color
Great clarinetists may not always say “I practiced the E Phrygian scale,” but you can hear this color glowing inside their phrasing, their turns, and their improvisations.
Anton Stadler, Mozart's muse, lived in a harmonic world where modes were always lurking below the surface. The chalumeau register of his basset clarinet naturally invites Phrygian gestures. Try playing the E Phrygian scale low on your modern Bb clarinet, and you will feel that connection to Stadler's rich, vocal tone.
Heinrich Baermann, for whom Weber wrote his legendary concertos, inspired passages that flirt with Phrygian tension. In the slow movement of Weber's Clarinet Concerto No. 1, you can hear melodic turns that, shifted to E and stripped of their harmony, outline Phrygian inflections, especially around semitone sighs.
Jump to the 20th century and the E Phrygian color explodes in jazz and crossover playing. Benny Goodman may be known for bright swing keys, but listen to his small-group recordings where he dips into Spanish-inflected tunes. When he slides from F down to E in a minor context, that is essentially an E Phrygian flavor shining through. Artie Shaw, with his liquid legato and daring chromaticism, often approached minor centers with that same flat-second bite.
On the classical concert stage, Sabine Meyer and Martin Frost are both masters of that dark, speaking half step. Hear Sabine Meyer's recordings of Debussy's Premiere Rhapsodie or Frost playing Anders Hillborg's Peacock Tales. Even when the key is not officially E Phrygian, the expressive slide and the hovering semitone between neighboring notes carry the same emotional weight as practicing this mode carefully in your long tones.
Then there are the klezmer and world-music clarinetists who practically live in Phrygian-inspired modes. Giora Feidman and David Krakauer spend entire choruses stretching a Phrygian or Freygish color, bending reeds in pieces like Der Heyser Bulgar or Krakauer's takes on traditional nigunim. On Bb clarinet, switching those ideas to E as a home note immediately throws you into the atmosphere of E Phrygian.
Where you secretly hear E Phrygian every day
Even if a score does not print “E Phrygian” at the top, your ear knows it. This scale appears in film scores, chamber music, and jazz standards that every clarinetist eventually touches.
Think of classic Spanish-style pieces often arranged for clarinet and piano. When you hear that intense minor flavor with a half step right above the tonic, there is Phrygian in the air. Play through an arrangement of Isaac Albeniz's Asturias or Francisco Tarrega's Recuerdos de la Alhambra and center your thinking on E with F natural just above it. Suddenly the clarinet part feels like an E Phrygian meditation even if the original guitar key is different.
Film composers lean on this sound constantly. In darker moments of scores by Ennio Morricone or Hans Zimmer, the low clarinet section often outlines a Phrygian mode around E or A. That tense, almost whispered line in the low clarinets in crash scenes or desert scenes often moves from F to E or B to A in a way that is pure Phrygian color.
In the jazz world, tunes like Spain by Chick Corea or arrangements of Malaguena commonly played in big bands give clarinetists and saxophonists space to improvise with modes that feel very close to E Phrygian once transposed. Clarinetists like Paquito D'Rivera often slide into Phrygian runs in their Latin jazz solos, especially in extended cadenzas or introductions.
Listen to Richard Stoltzman playing Argentinian tango arrangements or Astor Piazzolla transcriptions. The harmonic language loves that semitone tension, and if you map his phrasing onto E, you will hear E Phrygian written all over his bends and sighs, especially when he uses subtle vibrato and glissando over the break.
| Context | How E Phrygian shows up | What to listen for on clarinet |
|---|---|---|
| Flamenco-style pieces | Melodies built on E with F natural | Intense low-register lines, E-F semitone sighs |
| Klezmer tunes | Freygish and related modes | Ornamented F to E turns, crying bends |
| Modern film scores | Low clarinets on E-centered ostinatos | Slow, dark lines with half-step tension |
Why E Phrygian feels so emotional on Bb clarinet
Part of the magic lies in how this scale sits under your fingers. The E Phrygian scale on Bb clarinet runs through the chalumeau and clarion registers in a way that invites singing tone, warm air, and expressive finger motion across the break. It feels like a story climbing a staircase and then looking back over its shoulder.
Emotionally, E Phrygian sits somewhere between sadness and courage. The ear hears minor, but that flat second gives an extra twist of longing. Clarinetists use this when they want to sound ancient, introspective, or boldly Spanish. Think of a solo in a dark jazz club, a cadenza in a concerto, or a klezmer doina at a wedding at 2 a.m. This one mode can support all of that.
For expressive players like Sharon Kam or Kari Kriikku, who constantly tilt their sound between bright and shadowed colors, the Phrygian half step is an emotional spotlight. Practicing the E Phrygian scale slowly lets you control that spotlight on every note, from low E with full support to high B and C with focused embouchure and smooth throat tones.
Why mastering the E Phrygian scale matters for you
If you love improvisation, E Phrygian gives you a ready-made palette for Latin jazz vamps, rock and metal riffs, and modal jams. Guitarists often call this their “Spanish” sound. When you can run the E Phrygian scale effortlessly on Bb clarinet, you can join those jams without guessing which notes fit.
For classical and chamber players, E Phrygian practice sharpens your intonation and color control on semitones, especially the F to E and B to C steps. That pays off in Brahms symphonies, Debussy rhapsodies, and Reger sonatas where those small intervals carry huge emotional weight.
It also connects you directly to clarinet traditions in klezmer, Middle Eastern ensembles, and contemporary pieces. Many modern composers for clarinet, from Osvaldo Golijov to Jorg Widmann, lean on Phrygian hues to evoke history and folk memory. Your E Phrygian scale is your passport into that sound world.
| Practice focus | Benefit for your playing | Where you will feel it |
|---|---|---|
| Smooth E Phrygian long tones | Better tone and control in chalumeau | Mozart concerto, Brahms symphonies |
| Fast E Phrygian runs | Confident improvisation vocabulary | Jazz jams, Latin charts, klezmer sets |
| E-F semitone shaping | Stronger phrasing and emotional nuance | Slow movements, cadenzas, solos |
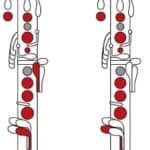
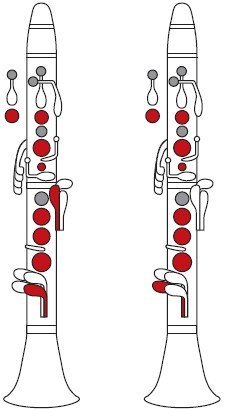
A few quick fingering notes for E Phrygian
The free clarinet fingering chart for the E Phrygian scale gives you every note, written and sounding, across the instrument. Most of the scale uses standard, comfortable fingerings: low E with all six fingers, F and G in chalumeau, and then across the break through A, B, and C in clarion.
The main technical focus is the shift between written B and C and the return down through A, G, and F to E. That pattern appears constantly in repertoire, from orchestral clarinet parts in Mahler to solo cadenzas in contemporary concertos. Use the chart to check your choices for alternate fingerings in the throat and clarion registers, especially when you want smooth slurs and clean articulation.
- Play the E Phrygian scale slowly with a tuner, holding each note for 4 beats.
- Repeat using legato slurs across the break from G to A and B to C.
- Practice short patterns like E-F-G and G-A-B-C up and down.
- Add simple rhythms you might hear in flamenco or klezmer tunes.
- Finish by improvising a 16-bar melody using only E Phrygian.
E Phrygian practice routine for Bb clarinet
Here is a simple practice plan that treats the E Phrygian scale as music, not homework. Use it as a starting point and color it with your own phrasing and dynamics.
| Exercise | Time | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Long-tone E Phrygian up and down | 5 minutes | Air support, intonation on F to E semitone |
| Two-octave scale with metronome | 5 minutes | Finger coordination, smooth break crossing |
| Small patterns (E-F-G, G-A-B-C) | 5 minutes | Even tone, relaxed hand position |
| Improvised melody over E pedal | 5 minutes | Expression, phrasing, dynamic contrast |
For extra inspiration, play along with recordings that use this color. Take a slow section from a Giora Feidman performance or a modal jazz track and gently weave your E Phrygian lines into the harmony. The goal is not accuracy at first, but connection and story.
Key Takeaways
- Use the E Phrygian scale to add Spanish and klezmer color to your Bb clarinet solos and improvisations.
- Practice the flat-second semitone (F to E) slowly to strengthen intonation and expressive phrasing.
- Let the free fingering chart guide your technique, but focus your ears on recordings by masters like Feidman, Krakauer, and Stoltzman.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Bb clarinet E Phrygian scale fingering?
The Bb clarinet E Phrygian scale fingering is the pattern of keys used to play the notes E, F, G, A, B, C, and D with E as tonic. It follows standard fingerings across chalumeau and clarion registers. Practicing this pattern helps develop smooth break crossing, accurate semitones, and a rich, Spanish-influenced sound palette.
How does the E Phrygian scale sound compared to E natural minor?
E Phrygian has a flat second (F natural) while E natural minor has F sharp. That single note changes the mood completely. E Phrygian sounds darker and more exotic, often associated with Spanish and Middle Eastern music. On Bb clarinet, it feels like a slow burn instead of a straightforward sad song.
Why should a beginner clarinetist practice the E Phrygian scale?
Even beginners can benefit from E Phrygian. It uses comfortable fingerings in first and second registers, and it trains the ear to hear and control semitones, especially F to E. It also opens the door to simple improvisation over backing tracks, making practice feel more like real music and less like just exercises.
Which famous clarinetists use Phrygian-style lines in their playing?
Giora Feidman and David Krakauer often use Phrygian and related modes in klezmer performances. Jazz players like Paquito D'Rivera and Artie Shaw touch this color in Latin tunes and minor ballads. Classical soloists such as Sabine Meyer and Martin Frost shape similar semitone tensions in modern concertos and expressive rhapsodies.
How can I use E Phrygian in improvisation on Bb clarinet?
Use E Phrygian over chords that center on E minor or Spanish-style progressions. Start by playing simple stepwise melodies from E up to D and back, focusing on F natural for tension. Add rhythmic patterns, glissando between notes, and dynamic swells, just as Giora Feidman or a flamenco guitarist might sculpt a solo.
For more on clarinet color and scales, you can continue with guides like the Martin Freres Bb clarinet fingering chart collections, their articles on classical clarinet tone development, and their historical notes on early French clarinet design. Let those stories sit beside your E Phrygian practice, and the scale will start to feel like an old friend.